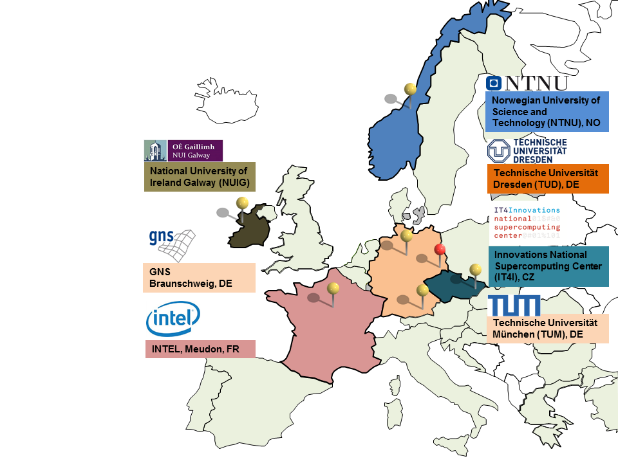
Seven partners from academia, HPC resource providers, and industry are working together in the READEX project.
Technische Universität Dresden
The TU Dresden is one of eleven German universities that were identified by the German government as an ‘excellence university’. As a modern full-status university with 14 departments it offers a wide academic range making it one of a very few in German.
The Center for Information Services and High Performance Computing (ZIH) is a central scientific unit of the TU Dresden with a broad spectrum of services and research activities. The ZIH supports other departments and institutions in their research and education for all matters related to information technology and computer science. In its mission to be a competence centre for scientific computing, parallel programming, and performance optimization, ZIH offers HPC resources to academic users as well as support for HPC application development. It also cooperates with other international HPC centres to assist users in enhancing their programs on highly parallel systems with more than 100,000 cores.
A European Project Center (EPC) has been established at TUD to support international project management.
Main attributed tasks of TU Dresden
- Development of PTF tuning plugins for hardware and software parameters
- Development of visualization of the detected dynamism using the Vampir graphical trace analysis tool-kit
- Creation of a low-overhead run-time library for identification of scenarios and setting of optimal parameters
- Financial, legal and administrative issues during the implementation of READEX
Links
https://tu-dresden.de
https://tu-dresden.de/zih/
Principal Investigator
Technische Universität München
Technische Universität München is one of the Excellence Universities of Germany. The Faculty of Informatics is one of the 13 faculties of the university.
The Chair on Computer Architecture (LRR) has been working in the field of parallel processing for over 20 years. LRR’s major research is in interactive runtime tools for parallel and distributed systems. LRR has developed performance analysers, debuggers, program flow visualizers, and the necessary online monitoring techniques. In addition, LRR investigates high-performance cluster computing as well as accelerated HPC architectures.
Main attributed tasks of TU München
- Development and implementation of design time analysis based on the Periscope Tuning Framework
- Contribution to the runtime detection of scenarios and the low-overhead switching of configurations in the runtime library
- Support the partners in working with PTF and Pathway
- Provide its knowledge on automatic tuning
Links
https://www.tum.de
http://www.lrr.in.tum.de
Principal Investigator
Norwegian University of Science and Technology
The Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU) is Norway’s premier university for higher education in technology and the natural sciences. NTNU has 7 faculties and 52 departments and more than 100 laboratories, many of which are national resources used both in research and teaching. It has research and education cooperation with more than 320 universities worldwide with prioritized geographical areas such as the EU, the USA, Japan, India and China.
The contributing departments, Department of Electronics and Telecommunications (IET) and Department of Computer and Information Science (IDI) are the two largest entities at Faculty for Information Technology, Mathematics and Electrical Engineering (IME). The IME has great influence on and responsibility for new information-based industrial developments and development within other areas of society, which apply information and communication technology.
Main attributed tasks of NTNU
- Applying knowledge in system scenario based design
- Develop energy efficient mechanisms for scenario identification, detection and switching
- Essential parts of the design-time and runtime mechanism
Links
http://www.ntnu.edu/iet
http://www.ntnu.edu/idi
Principal Investigator
Innovations National Computing Center
VSB-Technical University of Ostrava (VSB-TUO) was founded in 1849, it has since grown into a modern institution of higher learning, offering the highest levels of education in technical and economic branches of study.
IT4Innovations National Supercomputing Center (IT4I) is a part of VSB-TUO. IT4I was founded in July 2011 and consists of supercomputer centre and 8 research programmes divided into 3 categories: IT4People (focusing on improving the quality of life in society through modern information technologies), SC4Industry (focusing on supercomputing in solving industrial problems, modelling in the field of natural sciences, computational solid and fluid mechanics, and nano-technologies), Theory4IT (focusing on basic research, particularly on the development of new and non-traditional computational methods).
Main attributed tasks of IT4I
- IT4I specializes on research dealing with the design and massively parallel implementation of scalable hybrid solvers especially of FETI type
- The deployment of these solvers into the real engineering applications (Elmer, PERMON, ESPRESO, OpenFOAM)
- Comparison of the manual- and auto-tuning
Links
https://www.vsb.cz/en
https://www.it4i.cz/?lang=en
Principal Investigator
National University of Ireland, GALWAY
The National University of Ireland, Galway, founded in 1845, is the only university located in the Borders, Midlands and Western region of Ireland and has established a distinguished record in scholarship and research.
The Irish Centre for High-End Computing (ICHEC) is the national High-Performance Computing centre in Ireland, established in late 2005 under the aegis of NUI Galway. The ICHEC is pursuing an active policy of engagement and collaboration with the research community to support the development of internationally competitive computational modelling and world-class research across all the main disciplines. In its relatively short existence, ICHEC has supported over 700 projects and over 1000 researchers, and developed strong credentials in heterogeneous programming and capability computing.
Main attributed tasks of ICHEC
- Integration of all components into a first READEX prototype and software release
- Develop and establishing of appropriate measures to ensure software quality
- Evaluation of dynamicity exhibited by existing and future HPC applications
- Define of generic specification for providing domain-level knowledge about application dynamism
- Analysing the potential of application parameters.
Links
http://www.nuigalway.ie
http://www.ichec.ie
Principal Investigator
INTEL
Intel Corporation is the world’s largest semiconductor chip maker. Intel mission is to constantly push the boundaries of innovation in order to make people’s lives more exciting, more fulfilling, and easier to manage.
In 2010, Intel has partnered in the Exascale Computing Research (ECR) lab, a collaborative effort with CEA, Genci and the University of Versailles. The Intel team at the lab ECR is part of IPAG (Intel Path finding Architecture Group) Europe comprised of 4 labs, attached to DCG at Intel Corporation. IPAG is reporting to Diane Bryant, senior VP Data Center group. The Datacenter Group (DCG) drives new products and technologies from high-end co-processors for supercomputers to low-energy systems for datacenters, as well as solutions for cloud and big data. The group is a worldwide organization that develops the products and technologies that power nine of every 10 servers sold worldwide.
Main attributed tasks of Intel
- Support the collection and the analysis of data coming from RAPL, sensors and telemetry from Intel computing elements and from the Intel® Performance Counter Monitor
- Investigate the tuning parameters (hardware, software, application layers) on the node, and in particular with node exhibiting both coarse grain and fine grain computing elements
- Explore of parameter switching
- Connect READEX to existing power management solutions such as Intel® Datacenter Manager through API
- provide verification and metrics
Links
Principal Investigator
Marie-Christine Sawley
Gesellschaft für numerische Simulation mbH
GNS was established in 1995 and is one of the leading German providers of services and software in the area of finite element simulations, mainly for the international automotive, aviation and aerospace industry.
The company’s Finite Element Software Development department develops and maintains GNS’s software system Indeed, a specialized solver for obtaining highly accurate simulations of sheet metal forming processes that is primarily used in the automotive industry, and the associated pre- and post-processor OpenForm.
Main attributed tasks of GNS
- Use the finite element code Indeed to test the tools developed
- Testing of software and problem resolution
- Suggesting further improvements and evaluating their capabilities
Links
Principal Investigator
Kai Diethelm